Network Workbench (NWB) Tool v0.2.0
Release Notes
by Weixia (Bonnie) Huang
October 30th, 2006
1. General Description
The Network Workbench (NWB) Tool (v0.2.0 release) is a network analysis, modeling and visualization toolkit for biomedical, social science and physics research. It is a standalone desktop application requiring JAVA 1.4+ JRE. The tool installs and runs on Windows and Linux x86.
It is
using Cyberinfrastructure Shell
(CIShell)
v0.2.1 to integrate various datasets and algorithms. Although CIShell is developed using JAVA, it can integrate
algorithms developed by other programming languages such as FORTRAN, C, and
C++.
2. Downloading, Installing and Uninstalling
Download the NWB tool v0.2.0 and make sure to save the download as a jar file.
To install the NWB tool, simply double click the jar file, or run the command line java -jar nwb-installer_0.2.0.jar.
To uninstall the NWB tool, go to program (or application) menu, find “Network Workbench” program group, click “Uninstall NWB”. Another option is to go to the directory “nwb_installation_dir/Uninstaller” and double click uninstaller.jar.
3. What’s New
3.1. File Formats
The tool can load, process, and save four file formats:
· GraphML (*.xml)
· XGMML (*.xml)
· Pajek .NET (*.net)
· NWB (*.nwb)
The tool also supports viewing and saving of plain text files generated by algorithms.
For detail information about the above file formats, please visit the NWB Community Wiki.
3.2. Algorithms
The tool provides 41 network analysis, modeling, and visualization algorithms. Half of them are developed using FORTRAN, while the rest of them use JAVA. Detailed algorithm descriptions are available at the NWB Community Wiki. Here is the complete algorithm list in the v0.2.0 release.
|
Category |
Algorithm |
Language |
|
Preprocessing |
Directory Hierarchy Reader |
JAVA |
|
Modeling |
Erdös-Rényi Random |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Barabási-Albert Scale-Free |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz Small World |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Chord |
JAVA |
|
|
CAN |
JAVA |
|
|
Hypergrid |
JAVA |
|
|
PRU |
JAVA |
|
Analysis |
Attack
Tolerance |
JAVA |
|
|
Error
Tolerance |
JAVA |
|
|
Betweenness Centrality |
JAVA |
|
|
Site Betweenness |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Average
Shortest Path |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Connected
Components |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Diameter |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Page Rank |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Shortest
Path Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz Clustering Coefficient |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz Clustering Coefficient Versus Degree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Directed
k-Nearest Neighbor |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Undirected
k-Nearest Neighbor |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Indegree Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Outdegree Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Node Indegree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Node Outdegree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
One-point
Degree Correlations |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Undirected
Degree Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Node
Degree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
k
Random-Walk Search |
JAVA |
|
|
Random
Breadth First Search |
JAVA |
|
|
CAN
Search |
JAVA |
|
|
Chord
Search |
JAVA |
|
Visualization |
Tree Map |
JAVA |
|
|
Tree Viz |
JAVA |
|
|
Radial Tree
/ Graph |
JAVA |
|
|
Kamada-Kawai |
JAVA |
|
|
Force
Directed |
JAVA |
|
|
Spring |
JAVA |
|
|
Fruchterman-Reingold |
JAVA |
|
|
Circular |
JAVA |
|
|
Parallel
Coordinates (demo) |
JAVA |
|
Tool |
XMGrace |
|
Table 1: A list of algorithms in the NWB Tool v0.2.0
3.3. Converters and Conversion Service
The tool provides a set of converters and a conversion service tying them together that automatically transforms data from one format to another. When invoked, the conversion service will try to find a chain of converters that can transform the input data format to one that an algorithm can accept. Figure 1 shows the conversion graph supported by the NWB tool v0.2.0 release.
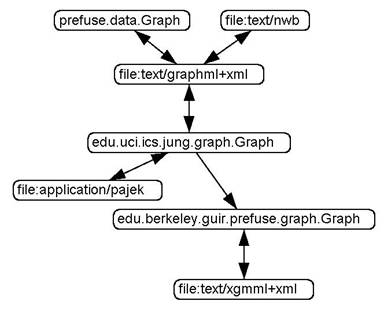
Figure 1: Conversion Graph in the NWB Tool v0.2.0
3.4. Other Features
· Sample Data: The tool provides several sample datasets in nwb_installation_dir/sampledata/Network.
· References and Documentations of Algorithms: When a user selects an algorithm from the menu, the acknowledgement will appear in the console. The acknowledgement information contains the original authors of the algorithm, the developers, the integrators, a reference, and the URL to the reference if available. Furthermore, the acknowledgement includes a URL to the algorithm description at the NWB community wiki website at https://nwb.slis.indiana.edu/community.
4. Known Issues
This list covers some of the known problems with NWB Tool v0.2.0. Please read this before reporting any new bugs.
· XMGrace: the tool provides a plugin that can invoke xmgrace --- a WYSIWYG 2D plotting tool to plot analysis results. This plugin exclusively works in the Linux environment. In order for the plugin to work, the tool requires a working installation of the Grace package.
· Visualization Algorithms: All visualization algorithms except the xmgrace plugins and Parallel Coordinates (demo) are developed using Prefuse alpha and JUNG libraries. Therefore, these visualization algorithms do not visualize large-scale networks. To our knowledge, it takes excessive time to visualize a graph with over 1000 nodes and the algorithms can not handle a graph with over 5000 nodes in general.
· Algorithm Performance: Those algorithms developed in FORTRAN are more scalable and efficient when comparing to JAVA-based implementations. They can generate and deal with large networks with over 1,000,000 nodes.
· Stop a Running Algorithm: This release does not have a scheduler --- a module that allows users to stop/pause/resume a running algorithm. This feature will be implemented and delivered in the next release on December 22nd, 2006.
· Directed vs. Undirected Networks: Many analysis algorithms in this release can only deal with undirected networks. When a user tries to apply those algorithms to a directed network, they will generate an error messages such as “Error! The program should be applied on directed networks.” We will make the improvement in the next release so that algorithms that can only apply to direct networks won’t be selectable when an undirected network is given as input.
· Run on Mac OS X PPC: The tool can be installed and run on Mac OS X PPC. On the other hand, without thorough testing, there are some problems in this release. For instance, all visualization algorithms don’t work on Mac because they use AWT or Swing. The web page at http://www.eclipse.org/swt/faq.php#swtawtosx explains the reason. Fileà view may or may not work depending on the platform setup as well as null pointer exceptions when the tool starts up. We would appreciate bug reporting by sending us the console log messages.
5.
Icons
The NWB tool uses the following icons to represent different datasets:
![]() Network
Network
![]() Tree
Tree
![]() Plain text file that can be plotted using xmgrace
Plain text file that can be plotted using xmgrace
![]() Other text file
Other text file
![]() Unknown file format or data format
Unknown file format or data format
6.
Report Bugs
Please report bugs to Weixia (Bonnie) Huang by email:
![]()