Network Workbench (NWB) Tool v0.8.0
Release Notes
Dec 21st, 2007
1. General Description
The Network Workbench (NWB) tool (v0.8.0 release) is a network analysis, modeling, and visualization toolkit for biomedical, social science, and physics research. It is a standalone desktop application requiring Java 1.4+ JRE. The tool installs and runs on multiple platforms (see section 3.1 for details).
It uses the Cyberinfrastructure
Shell (CIShell) to integrate
various datasets and algorithms. Although CIShell is developed using Java, it
can integrate algorithms developed in other programming languages such as
FORTRAN, C, and C++.
2. Downloading, Installing and Uninstalling
Download the NWB tool v0.8.0 and make sure to save the download as a jar file.
To install the NWB tool, simply double click the jar file, or run the command line java -jar nwb-installer_0.8.0.jar or java -jar nwb-web-nstaller_0.8.0.jar
To uninstall the NWB tool, run Uninstall NWB from your operating system program menu or run uninstaller.jar (in NWB Install Directory/Uninstaller).
3.
What’s
New
3.1.
Full
Installer vs. Web Installer
In this release we continue providing a full installer nwb-installer_0.8.0.jar (size 62.5MB) that can run on Windows
XP, Linux x86, and Mac OS X (PowerPC and Intel).
We also provide a new web installer nwb-web-installer_0.8.0.jar (size 1.18MB)
that supports to install NWB tool on Windows XP, Windows
Vista, Linux x86, Solaris, and Mac OS X (PowerPC and Intel).
Note:
·
The
web installer is under testing right now. Please report any installation
problem to nwb_helpdesk@googlegroups.com.
·
During
installing the NWB tool, the web installer requires Internet connection and can
automatically detect your local operating system and download the platform
specific package (size 62MB).
·
To
run the NWB tool on Windows Vista, your only option is to
download and run the web installer.
·
All
non-Java based algorithms, especially all algorithms written in FORTRAN (see
table 1 in section 4.2) are NOT pre-compiled on Solaris and Windows Vista
platforms.
So they may not run properly on those platforms. We will fix this problem in
the next release.
3.2.
New
Algorithm Plug-ins and Improvements:
·
Added
several plug-ins to support a prototype of loading an ISI file, extracting a
co-authorship network, and updating the co-authorship network by merging nodes (authors
with different names). A tutorial on this topic will be available soon.
·
Added a
plug-in to integrate GUESS – a graph exploration
system. Note: This plug-in works on Mac
and Linux but does not work on Windows. We will try to fix the problem before
the next release.
·
Added
Balloon Graph visualization algorithm.
3.3.
New
Data Converters, File Loader and Improvements:
·
Created
a converter to converter Prefuse beta-version Tree to Prefuse alpha-version
Tree.
·
Supported
to load an ISI file.
·
Supported
to load and automatically clean an ISI file.
·
Supported
to load GraphML format with file extension of *.graphml
·
Re-implement
nwb to graphml converter using XMLStreamWriter.
·
Many fixes in various converters.
3.4.
Community
Improvements
·
New mailing lists
nwb_announce@googlegroups.com
is a very low traffic mailing list for
announcements regarding the NWB project and software releases, mostly release
notes and important updates.
nwb_helpdesk@googlegroups.com
is the main mailing list for the NWB community.
Subscribe to this list to participate in the project, ask for help, report
bugs (temporary solution), talk about NWB-related matters.
nwb_dev@googlegroups.com
is NWB development mailing list. Subscribe to this
list and take part in the NWB development, talk about NWB-development related
matters or to keep up to date with NWB development.
·
NWB trac system
If you
are interested in our development activities, the new features we are working
on, the planned software releases, etc, please visit https://cns-trac.slis.indiana.edu/trac/nwb. We apology for closing the
functionality to allow people using anonymous account to submit bugs/tickets to
http://cns-trac.slis.indiana.edu/trac/nwb
right now since the website got spammed. We will re-open our bug tracking
system to the world soon. Please report bugs to nwb_helpdesk@googlegroups.com
temporarily.
·
SVN repositories
The
source code of all algorithm and converter plug-ins in the NWB tool is
available at http://nwb.slis.indiana.edu/svn/nwb.
CISshell
framework source code is available at https://cishell.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/cishell.
4.
Features
4.1. File Formats
The tool can load, process, and save the following file
formats:
GraphML (*.xml or *.graphml)
XGMML (*.xml)
Pajek .NET (*.net)
Pajek .Matrix (*.mat)
NWB
(*.nwb)
TreeML (*.xml)
CSV (*.csv)
ISI (*.isi)
The tool supports viewing and saving of plain text files
generated by algorithms.
The tool can load and process an edge
list with two columns (*.edge) but can’t save as an edge list.
For detailed information about the above file formats, please visit the NWB
Community Wiki.
4.2. Algorithms
The tool provides over 60
network analysis, modeling, and visualization algorithms. They are developed
using FORTRAN, Java, Perl, ocaml, etc. Detailed algorithm descriptions are
available at the NWB
Community Wiki. Here is the complete algorithm list in the v0.8.0 release.
Other algorithms not including
in the release are also available for downloading from NWB repository at http://nwb.slis.indiana.edu/svn/nwb
|
Category |
Algorithm |
Language |
|
Load |
Load and
Clean ISI File |
Java |
|
|
Load CSV
Files |
Java |
|
|
Directory Hierarchy Reader |
Java |
|
Preprocessing |
Random Node Deletion (Error Tolerance) |
Java |
|
|
High
Degree Node Deletion (Attack Tolerance) |
Java |
|
|
Pathfinder
Network Scaling |
Java |
|
|
Multipartite
Joining |
Java |
|
|
Snowball
Sampling |
Java |
|
|
Node
Sampling |
Java |
|
|
Edge
Sampling |
Java |
|
|
K-Core
Extraction |
Java |
|
|
K-Coreness
Annotation |
Java |
|
|
ISI
Duplicate Remover |
Java |
|
|
Extract
Co-Authorship Network |
Java |
|
|
Merge
Nodes |
Java |
|
Modeling |
Erdös-Rényi Random Graph |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Barabási-Albert Scale-Free |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz Small World |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Chord |
Java |
|
|
CAN |
Java |
|
|
Hypergrid |
Java |
|
|
PRU |
Java |
|
|
TARL |
Java |
|
Analysis |
Node
Degree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Degree
Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Undirected
k-Nearest Neighbor |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz
Clustering Coefficient |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Watts-Strogatz
Clustering Coefficient Versus Degree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Diameter |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Average
Shortest Path |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Shortest
Path Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Node
Betweenness Centrality |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Connected
Components |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Weak
Component Clustering |
Java |
|
|
Node
Indegree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Node
Outdegree |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Indegree
Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Outdegree
Distribution |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Directed
k-Nearest Neighbor |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Single
Node In-Out Degree Correlations |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Page Rank |
FORTRAN |
|
|
Burst
Detection |
Java |
|
Search |
CAN
Search |
Java |
|
|
Chord
Search |
Java |
|
|
k
Random-Walk Search |
Java |
|
|
Random
Breadth First Search |
Java |
|
Visualization |
Circular
(JUNG) |
Java |
|
|
Pre-defined
Positions (prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Radial
Tree / Graph (prefuse alpha) |
Java |
|
|
Radial
Tree / Graph with Annotation (prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Tree Map
(prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Tree View
(prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Balloon
Graph (prefuse alpha) |
Java |
|
|
Force Directed
with Annotation (prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Kamada-Kawai
(JUNG) |
Java |
|
|
Fruchterman-Rheingold
(prefuse alpha) |
Java |
|
|
Fruchterman-Rheingold
with Annotation (prefuse beta) |
Java |
|
|
Spring |
Java |
|
|
Small
World Visualization |
Java |
|
|
Parallel
Coordinations (demo) |
Java |
|
|
LaNet |
ocaml |
|
|
GUESS |
Jython/Java |
|
Tools |
Gnuplot |
|
|
|
Graph
Analysis Toolkit |
Java |
|
Other
plug-ins |
Scheduler
Tester |
Java |
|
|
Converter
Tester |
Java |
|
|
Graph to
Tables |
Java |
Table 1: A list of algorithms in the NWB Tool v0.8.0
4.3. Converters and Conversion Service
The tool provides a set of converters and a conversion
service that automatically transforms data from one format to another. The
conversion service tries to find a chain of converters that can transform the
input data format to one that an algorithm can accept. Figure 1 shows the core
conversion graph supported by the NWB tool v0.8.0 release. Figure 2 shows a
detailed conversion graph including many converters that
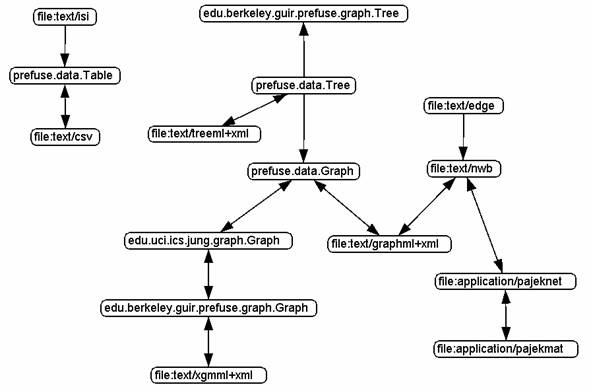
Figure 1: Core
Conversion Graph in the NWB Tool v0.8.0
4.4. Other Features
·
Sample Data: The tool provides several
sample datasets in NWB Installation Directory/sampledata.
· Working Completely on Mac OS X PowerPC and Intel. To make sure that all visualization algorithms using AWT or Swing work properly, NWB requires Java for Mac OS X 10.4, Release 5. Please go to the Apple website (http://docs.info.apple.com/article.html?artnum=304586) for details.
· References and Documentations of Algorithms: When a user selects an algorithm from the menu, an acknowledgement appears in the console. The acknowledgement contains the original authors of the algorithm, the developers, the integrators, a reference, and the URL to the reference if available. Furthermore, the acknowledgement includes a URL to the algorithm description at the NWB community wiki website at https://nwb.slis.indiana.edu/community.
· Scheduler: The Scheduler allows users to monitor the progress of running algorithms and to stop/pause/resume running algorithms that implement the scheduling API. A scheduler tester algorithm is provided to demonstrate the capabilities of the scheduler.
·
Invoke Gnuplot through the NWB tool:
the tool provides a plug-in that can invoke Gnuplot
--- a portable
command-line driven interactive data and function plotting utility. This plug-in works on Windows,
Linux, and Mac. To make the plug-in work on Linux and Mac, the tool
requires a working installation of the Gnuplot package. It has been packaged in
the NWB tool for Windows installation.
·
Graph Analysis Toolkit is a nice tool for getting the
insight of your datasets. It provides such rich information as number of nodes,
number of edges, the density of a graph, directed vs. undirected graph, whether
the graph has self-loops and/or duplicate edges, whether there’s a potential
error when a graph claims to be an undirected graph but has duplicate edges or
self loops, whether the graph has weakly connected components, whether the
graph has strongly connected components, etc.
5. Known Issues
This list covers some of the known problems with NWB Tool
v0.3.0. Please read this before reporting any new bugs.
· Algorithm Performance: Algorithms developed in FORTRAN are more scalable and efficient when comparing to Java-based implementations. They can generate and deal with large networks with over 1,000,000 nodes, which Java algorithms generally cannot.
·
Visualization Algorithms: The Kamada-Kawai and Fruchterman
Reingold algorithms cannot handle networks with 1000 nodes because the algorithms themselves have high complexity. It
takes excessive time for JUNG-based visualization
algorithms, including Circular and Spring Layout, to visualize a graph
with over 1000 nodes and they cannot handle a graph with over 5000 nodes in
general.
·
Stop a Running Algorithm: Although the new scheduler allows users to stop/pause/resume
a running algorithm, only algorithms written in Java that implement the ProgressTrackable
interface can be controlled by the scheduler. So far, only a few algorithms
integrated in the tool implement this interface. A scheduler tester algorithm
under FileŕTest is provided to demonstrate
the capabilities of the scheduler.
6.
Icons
The NWB tool uses the following icons to represent different
datasets:
![]() Network
Network
![]() Tree
Tree
![]() Plain text file that can be plotted using gnuplot
Plain text file that can be plotted using gnuplot
![]() Other text file
Other text file
![]() Unknown file format or data format
Unknown file format or data format
7.
Report
Bugs
Please report bugs to nwb_helpdesk@googlegroups.com temporarily.
We apology for closing the functionality to allow people using anonymous
account to submit tickets to http://cns-trac.slis.indiana.edu/trac/nwb
right now since the website got spammed. We will re-open our bug tracking
system to the world soon.